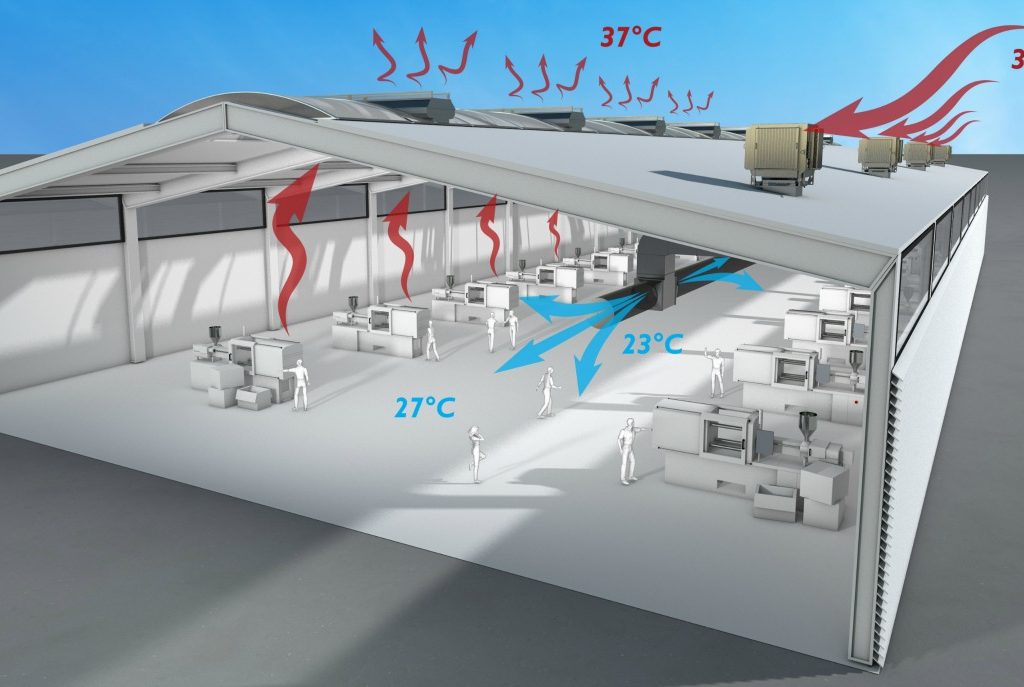
Advanced Evaporative Cooling Systems
Mist and fog are both created by water droplets, differing mainly in their overall density and locations. Fog is a cloud that reaches ground level, even if that "ground" is a hill or mountaintop. Mist forms wherever water droplets are suspended in the air by temperature inversion, volcanic activity, or changes in humidity.
Mist and fog differ by how far you can see through them. Fog is when you can see less than 1,000 meters away, and if you can see further than 1,000 meters up to 2000 meters we call it mist.
| FOG System | Mist System | |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Fog is a cloud that reaches ground level | Mist forms wherever water droplets are suspended in the air by temperature inversion, volcanic activity, or changes in humidity |
| Density | High | Medium |
| Visibility | Restricted less than 1,000 meters | Restricted 1,000 meters up to 2000 meters |
| Longevity | It lasts for a longer period | It lasts for a short period |
| Source | Water droplets | Water droplets |
| Nozzles | Stainless Steel or Ni Brass Nozzles | Stainless Steel or Ni Brass Nozzles |
| Pipes | Stainless Steel 316 L or Nylon Pipes | Stainless Steel 316 L or Nylon Pipes |
| Fans | Not Required | Required |
| Pumps | Required | Required |
| Benefits | Advanced technology used to enhance HVAC equipment efficiency for Humidification | Advanced technology used to enhance HVAC and irrigation equipment efficiency and reduce electrical power supply for HVAC equipment |
| Future Goals | Enhance equipment efficiency up to 30% | Enhance equipment efficiency up to 30% |
Definition of Fog
Fog is condensed water vapour suspended in the atmosphere, close to the earth’s surface, which forms an opaque sheet that restricts the visibility. It is a complex phenomenon of the atmosphere, that is greatly affected by neighboring water bodies, wind speed, topography, etc.
Air could hold a certain amount of water and the warmer it is, the more water it can carry. The more water fills the air, the more it becomes humid and after a certain point it starts cooling down and as the temperature reaches the dew point, it starts condensing, and fog is formed. dew point is the temperature at which relative humidity reaches 100%, air parcels reach saturation, and water vapor can condense. At 100% relative humidity, the dew point is equal to the air temperature.
There are many ways to calculate dew point. One easy way to approximate dew point is with a simple equation: T(dp) = T - ((100 - RH)/5).
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air, generally measured by mass (g or kg). Relative humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air vs the maximum amount of water vapor that can be in the air. Dew point is the temperature at which relative humidity reaches 100% and air is saturated.
Definition of Mist
water mist system is an advanced technology that uses small water droplets to control, suppress, or extinguish fires , Also used for cooling , dust control and etc.
Mist is an atmospheric phenomenon formed by tiny water vapour suspended in the atmosphere, at the surface of the earth that hinders visibility to some extent. This is caused by temperature inversion, volcanic activity, change in humidity. The chemical process that changes water globules to mist is called dispersion.
Mist is often observed when warm, moist air experience abrupt cooling, i.e. the droplets becomes visible to us when warm water droplets are suddenly cooled down. The most common example of mist is exhaled air during winters.
How to Implement FOG for Different Applications ?

Required Design then supply and install pumps, nozzles, stainless steel pipes, temperature, or humidity control.
Fog system commonly used for the following :
- Special Effects
- Humidification
- Fountains
How to Implement Mist for Different Applications?

Required Design then supply and install pumps, nozzles, stainless steel pipes, fans, temperature, or humidity control.
Mist system commonly used for the following :
- Irrigation
- Fountains
- Dust Control
- Outdoor Cooling
- Precooling Mist system for Split units Condensers intake air
- Precooling Mist system for VRF – VRF Condensers intake air
- Precooling Mist system for package units Condensers intake air
- Precooling Mist system for Air Cooled Chillers Condensers intake air
Key Differences Between Fog and Mist
The points given below are substantial, so far as the difference between fog and mist is concerned:
- A thick, low-lying cloud, which occurs at the earth’s surface, that is composed of tiny water droplets, suspended in the air, is known as Fog. Mist is defined as the cloud created when water globules are suspended in the air due to change in humidity or temperature inversion.
- Mist and fog greatly differ regarding density, as fog is much denser than mist, i.e. fog creates an opaque sheet, that blurs visibility.
- Fog obscures visibility to a greater extent than mist i.e. in the case of fog visibility will be different
- When it comes to longevity, mist lasts for short duration and tend to disappear quicker, with slight winds. On the contrary, fog lasts for several minutes or even hours and do not dissipate easily.